Transact-SQL query to display the list of all table names from a database with size and disk space used on the server.
Listing SQL Server table size and disk space can be very convenient specially to analyse the disk usage for each table. Three different ways, but similar are presented here to display SQL Server tables and disk space used by each table. The third solution also shows the number of lines for every table. Check out these SQL Server queries to display the list of SQL Server tables and their size in different ways.
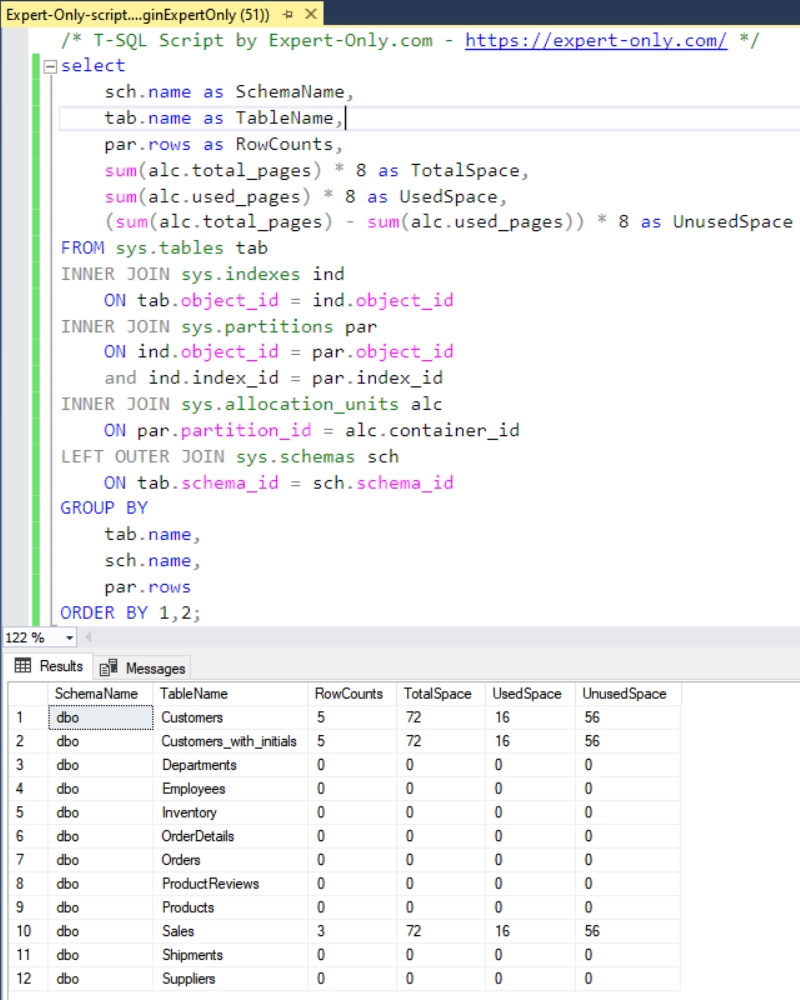
This third query is using different system tables joined together, namely sys.tables, sys.indexes, sys.partitions, sys.allocation_units and sys.schemas. It displays the schema name, the table name, the row counts and the disk space (total, used and unused space) for each table in a SQL Server database.
Table of Contents
1. SQL Server disk space usage is a classical maintenance topic
To go further, usually the goal is to check and free up disk space on the server hosting the database. Typically when the server hard drive is getting full, then this query displays the last time a table was accessed or updated. It’s very useful before deletion. For instance, if a table have not been accessed over the last three years, it might not be necessary anymore.
select sch.name as SchemaName, tab.name as TableName, par.rows as RowCounts, sum(alc.total_pages) * 8 as TotalSpace, sum(alc.used_pages) * 8 as UsedSpace, (sum(alc.total_pages) - sum(alc.used_pages)) * 8 as UnusedSpace FROM sys.tables tab INNER JOIN sys.indexes ind ON tab.object_id = ind.object_id INNER JOIN sys.partitions par ON ind.object_id = par.object_id and ind.index_id = par.index_id INNER JOIN sys.allocation_units alc ON par.partition_id = alc.container_id LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.schemas sch ON tab.schema_id = sch.schema_id GROUP BY tab.name, sch.name, par.rows ORDER BY 1,2;
Indeed, any database grows, because the log grows, the data grows, the log file grows, the backup file grows, etc. To fix this it’s mandatory to schedule maintenance scripts to clean the log tables and regularly delete the obsolete data, like for example five years rolling period to keep on line. For compliance legal reasons, depending on the business area, the data might need to be kept and backed-up more years.
2. Get the Size of all Tables in SQL Server using system views
This approach is to use the data stored in the information_schema schema about the tables. The Microsoft SQL query uses the information_schema.tables system table to display all the attributes and metadata from the system database. It displays the four columns available in the tables system view:
- TABLE_CATALOG is the database name.
- TABLE_SCHEMA is the schema hosting the table, per default it is database owner (dbo).
- TABLE_NAME is the name of the table.
- TABLE_TYPE is the table type.
Note that we filter the query on the view to display only the base table type. Other table types can also be View.
SELECT TABLE_CATALOG, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, TABLE_TYPE FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_type='base table';
3. List all SQL Server tables using system tables
To display SQL Server tables size and disk space, you can also run this last query in SSMS. This one uses the sys.tables system table, it is certainly the source of the system view used in the first query. It shows much more information’s and metadata. Like for example the creation data, the modification date, and the object_id reusable in other system functions and procedures.
-- Use the sys.tables system table SELECT * FROM sys.tables WHERE [type_desc] = 'USER_TABLE';
4. Get a list of all SQL tables from sys.tables
The last query uses the sys.tables system table. Certainly the source of the system view used in the first query. It shows a lot more information and metadata, like the creation data, the modification date, and the object_id which can be reused in other system functions and procedures.
-- Use the sys.tables system table SELECT * FROM sys.tables WHERE [type_desc] = 'USER_TABLE';
About listing tables and their attributes using T-SQL
In conclusion, this blog article presents several methods for display a list of all the user tables in a SQL Server database and their size. Displaying the size of the tables and the disk space used is useful for analysing the use of each table, which table, which can help to optimise disk space and improve database database performance.
To go further in the SQL Server database maintenance topic, check out this short tutorial on how to empty the transaction log to free up disk space with a Shrink Database script.




Be the first to comment