To audit a MSSQL database and its tables, it is common to want the list of tables in the form of a table or an Excel spreadsheet. This SQL query allows you to list all the tables in a SQL Server database and display the number of rows and size for each table. SQL Server developers also often look for tables, for example for impact analysis. Hence it is very useful to quickly list all the tables for an audit for example, whether it is technical or functional. To begin with, these three different T-SQL queries allow you to display the information in different ways, and with different levels of details.
- The first is a simple list of tables.
- Second query displays useful information such as the object_id column, create_date and modify_date.
- The third query displays the schema, the number of rows and the disk space used by each table.
Indeed, the SQL Server system tables and system views contain useful metadata that describes the different objects in the database, including the tables of course. Thus, all the solutions presented in this article use system tables or views, such as:
- information_schema.tables
- sys.tables
- sys.indexes
- sys.partitions
- sys.allocation_units
- or sys.schemas
Table of Contents
1. Display a list of all tables using one SQL Server system table
In SQL Server, information_schema.table is a view, not a table. It is one of the INFORMATION_SCHEMA views standardised by ISO for relational database management systems (RDBMS). This view provides information about the tables and views present in a database. You can consult it to obtain metadata on these tables and views, such as their names, types (table or view), and other details. For example, you can use the system table information_schema.table, like this:
SELECT * FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_type='BASE TABLE';
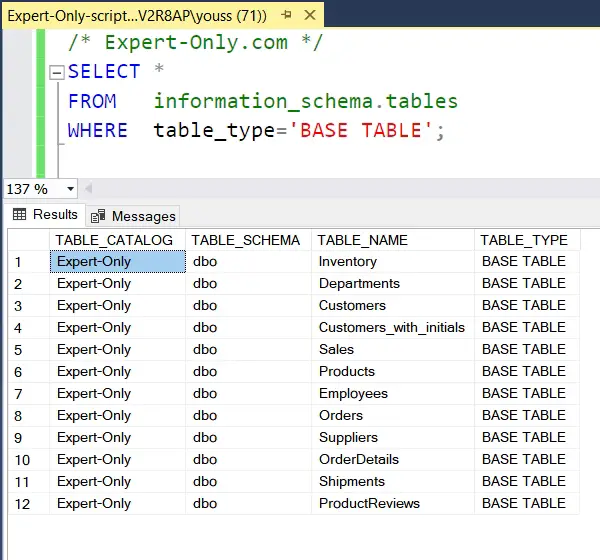
2. Query to get the list of SQL Server tables using sys.tables view
You can also use the sys.tables system table. The result of the query shows that the table type stored in the [type_desc] column is USER_TABLE. Sys.tables in Transact-SQL is also a system view and not a table. It is part of the SQL Server system catalogue and provides information on all the user tables and system tables that exist in the current database. It can be used to retrieve various details and metadata about tables, such as their name, creation date, modification date and so on. Although it can be queried as a table, do not treat it as an editable user table. Instead, it is a structured view that presents certain system metadata about the tables.
SELECT * FROM sys.tables;
3. Display the list of table names and sizes in T-SQL
The third one is to use multiple SQL Server system tables such as sys.tables, sys.indexes, sys.partitions, sys.allocation_units and sys.schemas. These tables are useful for displaying the list of tables. They are also used to display the number of rows in each table and the disk space used. For example, this query displays all tables with their number of rows sorted in descending order. This query is useful to find the size of the largest tables in a SQL Server database.
SELECT sch.name AS SCHEMANAME, tab.name AS TABLENAME, par.rows AS ROWCOUNTS, SUM(alc.total_pages) * 8 AS TOTAL_SPACE, SUM(alc.used_pages) * 8 AS USED_SPACE, (SUM(alc.total_pages) - SUM(alc.used_pages)) * 8 AS UNUSED_SPACE FROM sys.tables tabSELECT sch.name AS SCHEMANAME, tab.name AS TABLENAME, par.rows AS ROWCOUNTS, SUM(alc.total_pages) * 8 AS TOTAL_SPACE, SUM(alc.used_pages) * 8 AS USED_SPACE, (SUM(alc.total_pages) - SUM(alc.used_pages)) * 8 AS UNUSED_SPACE FROM sys.tables tab INNER JOIN sys.indexes ind ON tab.object_id = ind.object_id INNER JOIN sys.partitions par ON ind.object_id = par.object_id AND ind.index_id = par.index_id INNER JOIN sys.allocation_units alc ON par.partition_id = alc.container_id LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.schemas sch ON tab.schema_id = sch.schema_id GROUP BY tab.name, sch.name, par.rows ORDER BY par.rows DESC;
This list of bullets points explains the query above and how it is build.
- The keyword “ORDER BY par.rows DESC;” is used to sort the list of SQL Server tables by their number of rows, in a descending order.
- To sort by schema and then by table name, use “ORDER BY 1,2” or “ORDER BY sch.name, tab.name; ” instead.
- The size of the tables is noted in KiloBytes or KB.
About SQL Server object listing and system tables
This technical MS SQL Server tutorial explains how to create and use a query to list all tables in a given database. If you are still new to SQL Server and want to create a table, here is how to create a SQL Server table and insert a few rows of data. It is possible to display another list of MS SQL tables with more focus on disk space available.








Be the first to comment