Scripts examples using Python code to export SQL Server data from a table to a CSV file.
In this tutorial, we learn how to export data from a SQL Server table into a CSV file using only Python scripts and two dedicated python modules named pyodbc and csv. At the end of this relatively this relatively short and straightforward programming tutorial, you will know how to export data from a SQL Server database to a CSV file using Python. But first of course, you need a sample SQL table to export.
The 4 main steps to export data from SQL Server to CSV
- First one is to create a sample table in SQL Server using SSMS
- The second one is to connect to the SQL instance.
- Then retrieve data from the SQL Server table using a basic SQL select statement.
- And export the content of the table to a CSV file using the csv library in Python.
Table of Contents
1. Create a sample SQL Server table to export
This code creates a sample SQL Server table named dbo.employees in a database and inserts four sample rows. The table has four columns: id, name, department, and salary. And the id column is set as the primary key of the table. The INSERT INTO statements insert four rows of data into the dbo.employees table. Each row has values for each of the columns in the order they were specified, i.e. : id, name, department, and salary.
CREATE TABLE dbo.employees ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50), department VARCHAR(50), salary INT ); INSERT INTO employees VALUES (1, 'John Smith', 'Sales', 50000); INSERT INTO employees VALUES (2, 'Jane Doe', 'Marketing', 60000); INSERT INTO employees VALUES (3, 'Bob Johnson', 'IT', 70000); INSERT INTO employees VALUES (4, 'Alice Wong', 'HR', 55000);
2. Connect to SQL Server using Python and pyodbc
Indeed, technically the export to CSV file steps are very similar to the Excel export using Python, but this time the export module used in the next step is different. The first step is to connect to the SQL Server database using the pyodbc module. In my case i use a SQL Server 2019 installed on a Windows 10 machine. And I use Visual Studio 2019 to develop my Python scripts. Here is an example code that establishes a connection to a SQL Server database. I use a Windows authentication, so I do not need to enter a user name and a password.
# Import the pyodbc module to manage the odbc connection
import pyodbc
# Declare some variables to store the connections details
driver = 'SQL Server'
server = 'localhost'
database = 'Expert-Only'
# Connect to the local SQL Server database
connection = pyodbc.connect(f'DRIVER={driver};'
f'SERVER={server};'
f'DATABASE={database};'
f'Trusted_Connection=yes;')
Make sure to replace the placeholders with the actual values for your SQL Server connection string: driver, server, database, and if need be username and password. In this case the code would be more like this:
import pyodbc
# Connect to the SQL Server database
server = 'localhost'
database = 'database_name'
username = 'username'
password = 'password'
cnxn = pyodbc.connect('DRIVER={ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server};'
f'SERVER={server};'
f'DATABASE={database};'
f'UID={username};'
f'PWD={password}')
3. Retrieve the data from the SQL Server source table
Once the connection to the SQL Server database is established by the Python code, we can retrieve the data from the table using a T-SQL query. Here is an example code that retrieves all the rows from the dbo.employees table we created in the first step. Make sure to replace employees with the actual name of your SQL Server table, of course.
# Retrieve the data from the employees table
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM dbo.employees')
data = cursor.fetchall()
4. Python script to create the CSV file and export data from the table
Finally, we can create a CSV file using the csv module and write the data to it. Here is an example code that creates a new CSV file named employees.csv and writes the retrieved data to it. Once again, Make sure to replace the path and name to the file with the actual name that you want to give to your CSV file.
# Import the Python csv module
import csv
# Create a new CSV file and write data to it
with open("C:\data\employees.csv", mode='w', newline='') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerows(data)
5. Python code example to export SQL Server data in a CSV file
The full Python code example provided below demonstrates all the steps at once. Indeed, the script imports the 2 necessary libraries, i.e. pyodbc and csv and sets up a connection to the database. Then it executes a SQL query to select the data. And then writes the data to a new CSV file using the csv library.
The Python code extract the headers from the cursor description and write to the file first, followed by the data itself. Once the export is complete, the program closes the cursor and the database connection. Of course, modify this code is easy, for example to fit specific use case by adjusting the connection string, table name, and file name.
import pyodbc
import csv
# Step 1: Connect to the SQL Server instance
# declare some variables to store the connections details
driver = 'SQL Server'
server = 'localhost'
database = 'Expert-Only'
# connect to the local SQL Server database
connection = pyodbc.connect(f'DRIVER={driver};'
f'SERVER={server};'
f'DATABASE={database};'
f'Trusted_Connection=yes;')
# Step 2: Retrieve data from the SQL Server table
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM dbo.employees')
data = cursor.fetchall()
# Step 3: Write data to the CSV file
with open("C:\data\employees.csv", mode='w', newline='') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow([x[0] for x in cursor.description]) # write header
for row in data:
writer.writerow(row)
# Step 4: Close the database connection
cursor.close()
connection.close()
The result is a CSV file exported directly under the C:\data\ folder, with the same content as the original MS SQL table.
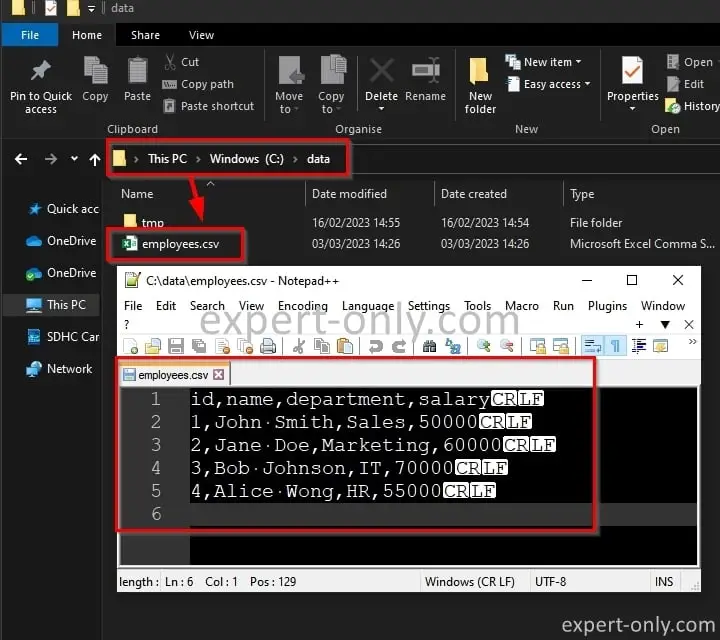
Of course , you also need to replace and set these variables with your own values:
- Driver
- Server
- Database
And if you are not using a Windows account that has access to the source database to execute the Python script:
- User name
- Password
About exporting data from SQL Server to CSV files using Python
In conclusion, after following all the 4 steps outlined in this Python tutorial, you should now be able export a SQL Server tables into CSV files using Python programming. Remember to first connect to your SQL Server database using pyodbc, then retrieve the data from the table, and finally write the data to a CSV file using the csv module. Exporting data from a SQL Server database to a CSV file can be a useful skill for many data analysis and reporting tasks, especially for repetitive tasks with large amount of data.
By automating this process with Python, you can save you hours of effort compared to doing it manually in Excel or other software. Indeed, Python provides a powerful set of tools for working with databases and data files.
More Python tutorials about data and file manipulations
- Export SQL Server table to Excel in Python
- Work with SQL Server using Python and pyodbc
- Manage text and csv files in Python using read and write methods
- How to zip and unzip files in Python ?




Be the first to comment